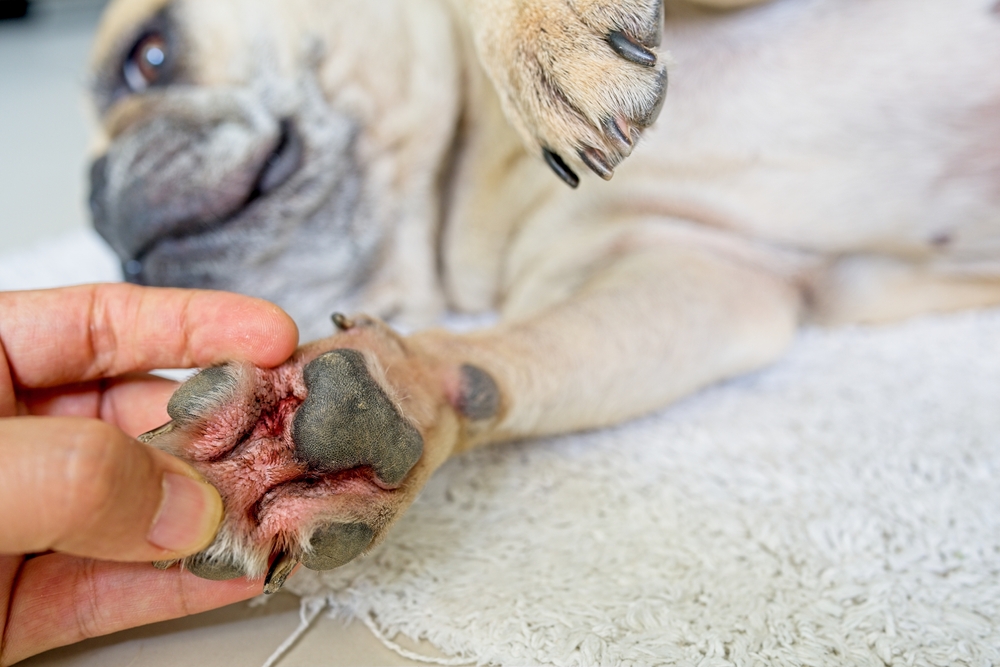
Skin diseases in dogs refer to a wide range of conditions affecting the health, appearance, and function of a dog’s skin. These diseases can manifest through symptoms like itching, redness, hair loss, sores, and irritation, and may be caused by allergies, infections, parasites, or underlying medical conditions.
There is some common categories of skin diseases in dogs include:
Allergic Dermatitis: Caused by allergies to environmental factors (like pollen, dust mites, or mold), food, or contact with irritants. This often results in itching, redness, and inflammation.
Parasitic Skin Diseases: Caused by fleas, ticks, mites, and other parasites. These infestations lead to itching, hair loss, and secondary infections from scratching.
Fungal and Bacterial Infections: Common infections like ringworm (fungal) or pyoderma (bacterial) lead to redness, swelling, sores, and sometimes odor.
Hormonal or Endocrine Disorders: Conditions like hypothyroidism and Cushing’s disease can cause skin abnormalities, such as hair loss, pigmentation changes, and skin thickening.
Autoimmune Skin Diseases: These are rare but serious conditions where the immune system attacks the skin cells, causing sores, lesions, and discomfort. Examples include pemphigus and lupus.
Seborrhea: A condition causing excessive skin scaling and greasiness, often due to a genetic disorder or underlying medical issues.
Here are 5 signs that indicate your dog may need a dermatologist visit:
1 – Persistent Itching or Scratching
If your dog is constantly scratching, licking, or biting at their skin, it could be a sign of a skin condition such as allergies, parasites, or infections. Persistent scratching often leads to secondary infections and may need specialized care.
2 – Red or Inflamed Skin
Red, swollen, or inflamed patches on the skin are signs of irritation that can stem from allergies, fungal infections, or even autoimmune conditions. If the skin looks inflamed and doesn’t improve with basic treatment, a dermatologist can help identify the underlying cause.
3 – Hair Loss or Bald Patches
Thinning fur, bald spots, or patches of hair loss can indicate issues like mange, hormonal imbalances, or allergies. A dermatologist can conduct tests to determine if there is a medical reason behind the hair loss.
4 – Sores, Scabs, or Lesions
Open sores or scabs can develop from excessive scratching or as a result of infections. Recurrent or non-healing lesions are often a sign that something more serious is at play, such as a bacterial or fungal infection.
5 – Changes in Skin Texture or Color
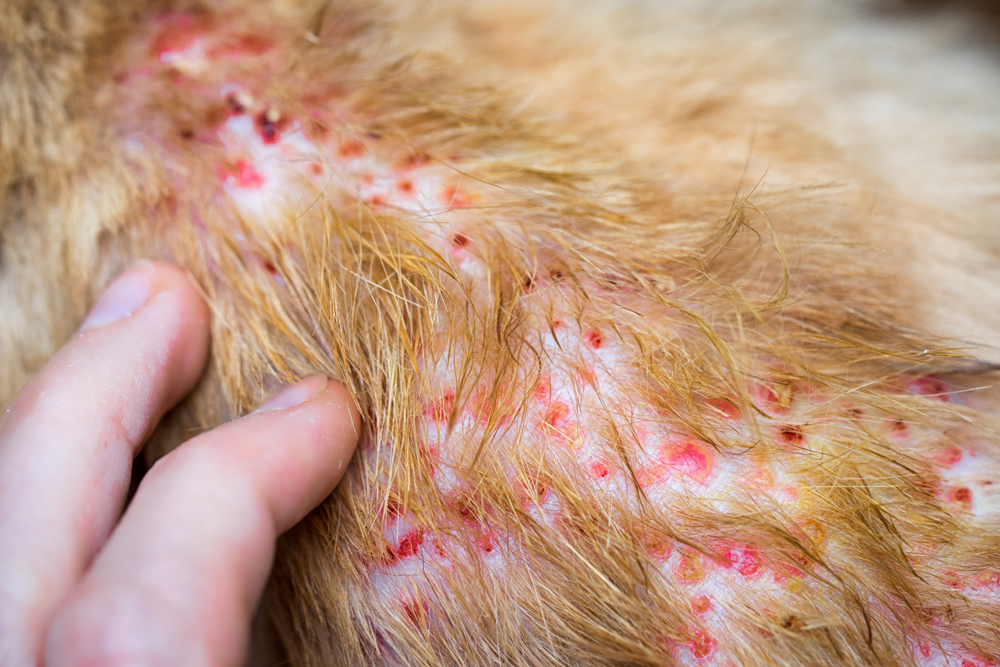
If your dog’s skin has areas that are thickened, rough, scaly, or discolored, these could be symptoms of chronic skin conditions, such as hyperpigmentation, dermatitis, or even skin tumors. Dermatologists can provide a more specialized diagnosis and treatment for these changes.
A visit to a veterinary dermatologist can help diagnose and treat these issues effectively, ensuring your dog remains comfortable and healthy.

